Java Notes
'while' Statement
Purpose - to repeat statements
The purpose of the while statement is to repeat
a group of Java statements many times. It's written just like
an if statement, except that it uses the
while keyword.
General Form
The while statement has this form:
while (condition) {
statements to repeat while the condition is true
}
Condition is true or false
The value of condition must be true or false
(ie, a boolean value). It is often a comparison (see example below).
Example: Loop continues while the condition is true
public void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
super.paintComponent(g);
int count = 0;
while (count < 50) {
g.drawLine(20, count*5, 80, count*5);
count = count + 1;
}
g.drawString("Loop is finished. count="+count, 10, 300);
}
This repeats the drawLine() call 50 times. The first time
the while condition is tested, it is true because
the value of count is 0, which is less than 50.
After the statements in the body are done, the while loop comes
back to the top of the loop and makes the test again.
Each time the value of count is larger.
Finally, count
is 50, and the value of the condition will be false.
When the loop stops, the program continues with the statement after
the end of the loop (the drawLine() call). This will display
the string "Loop is finished. count=50".
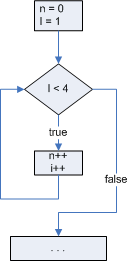
Example with flowchart
The following shows some code and the equivalent flowchart.
int n = 0;
int i = 1;
while (i < 4) {
n++;
i++;
}
. . .
|
|
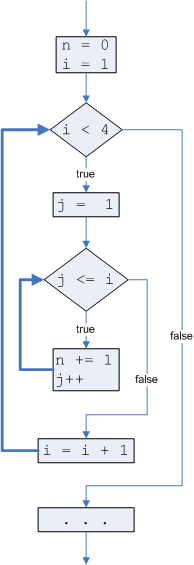
Here is another example of code and an equivalent flowchart
int n = 0;
int i = 1;
while (i < 4) {
int j = 1;
while (j<=i) {
n += 1;
j++;
}
i = i + 1;
}
|
|